- After nearly a year of negotiations with Turkey, Finland was approved for NATO membership;
- The country’s membership in the military alliance was a setback for Russia and its attempts to weaken NATO.
- The decision will have major impacts on geopolitics in the region, and could create even more tensions with Moscow.
On April 4, 2023, Finland officially joined NATO – North Atlantic Treaty Organization – as the 31st member, which represents a significant change in Europe’s security landscape, adding around 1,300 kilometers to the alliance’s border with Russia.
It is noteworthy that Sweden’s attempt to also join the bloc was stalled by alliance members Turkey and Hungary. However, the presidential elections in Ankara, which will take place in May 2023, could change this scenario in favor of Sweden, in case the current president, Recep Tayyip Erdogan, is defeated or significant political changes take place.
However, the geopolitical consequences can already be seen with Finland’s recent accession to the military alliance, which was sealed during a formal ceremony at NATO Headquarters in Brussels, Belgium.

How Russia’s Imperialist Mindset Encourages Other Countries to Join NATO
Russia’s imperialist mindset has created an environment in which neighboring countries and close allies feel the need to strengthen their own security and protect their sovereignty.
Russia has historically sought to extend its power and increase its sphere of influence, and this may raise concerns about the possibility of Russian interference or aggression in neighboring countries, especially after the invasion of Ukraine, which has been a concern for the country since Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014.
Finland’s recent entry into the US-led alliance is a setback for Russian President Vladimir Putin, who has long sought to weaken NATO and, before his invasion of Ukraine, demanded that the bloc refrain from further expansion towards to the Russian border.
However, the invasion resulted in the candidacy of Finland and Sweden to the alliance, which previously maintained a policy of non-alignment, abandoning their neutrality and seeking protection in the alliance.
Furthermore, Russia has been accused of interfering in the political affairs of other countries, which may heighten concern about the threat Russia poses and encourage cooperation with NATO. Georgia, for example, has been working to strengthen its ties with NATO since the 2008 Russo-Georgian War.
How Russia’s “NATO expansion” excuse for invading Ukraine doesn’t make much sense
The Russian claim that NATO expansion is the cause of the invasion of Ukraine is not coherent, as the expansion of the alliance was a voluntary decision of the member countries, Ukraine was never an official candidate for NATO membership and the invasion was a violation international law and Ukrainian sovereignty.
Another relevant element that demonstrates such a lack of coherence is Russian nuclear power. Russia is one of the countries with the largest nuclear arsenal in the world, which becomes a decisive factor for other states not to try to invade its territory.
However, the fact that Russia has a vast nuclear arsenal cannot be seen as a license for the country to advance beyond its borders. On the contrary, the possession of nuclear weapons should be a reason for a more responsible and cautious posture on the part of the State, in order to avoid actions that could have tragic consequences for all of humanity.
The invasion of Ukraine, under the pretext of protecting its own territory, ended up harming the country, since, in the second half of 2022, it was necessary to empty some of its military bases along the border with NATO countries such as Estonia, in order to send soldiers and equipment to the battlefield in Ukraine.
That is, if Russia were really worried about NATO armed aggression, it would not empty its bases that border the alliance to reinforce its troops against Kiev.
Furthermore, the Russian justification that NATO expansion is a threat to Russian national security is not tenable. NATO was created as a defensive alliance aimed at ensuring the security of member countries, and in theory, not to threaten other nations.
In addition, Russia has an aggressive foreign policy and has been involved in several actions that violate the sovereignty of other countries, such as the annexation of Crimea in 2014 and support for separatists in eastern Ukraine.
Therefore, the Russian justification that the invasion of Ukraine is due to the expansion of NATO is an unfounded reason that seeks to cover up Russia’s true motivation, which is the desire to expand its influence and power in the region and not let Ukraine prosper as a democracy. , which would likely lead the Russian population to demand the same freedoms and prosperity as the Russian elite. Such a move would be a threat to the power of Putin and his allies.
The geopolitical consequences of Finland’s entry into NATO
Finland’s entry into NATO will have important geopolitical consequences in the region and on the international stage.
Firstly, Finland’s membership has dramatically increased the Russian border with the military alliance, which is seen as an affront to Russia, which has historically regarded Finland as a buffer zone between NATO and the former Soviet Union. For this reason, Putin has already promised retaliation.
Furthermore, Finland’s entry is expanding NATO’s presence in the Baltic Sea, increasing its defense capability in the region and weakening Russia’s influence in the region and further isolating Kaliningrad – the Russian exclave in the middle of Europe – from the rest of the country.
Another notable consequence was the signing of a letter of intent between the air force commanders of Sweden, Norway, Finland and Denmark to create a unified Nordic air defense, with the aim of combating the growing threat from Russia and the intention is to be able to operate in set following the already known guidelines of operating under NATO.
Furthermore, Finland’s entry into NATO may increase pressure on Turkey to approve Sweden’s membership in the alliance. Sweden already cooperates closely with NATO on defense and security matters, but has yet to conclude its negotiations with Ankara.
Relations between the European Union and Russia could also be affected. Finland is a member of the EU and, although the organization does not have a common defense and security policy, Finland’s entry into NATO can be seen as a sign that the bloc is increasingly aligning itself with the interests of the military alliance. and the United States in the region, further straining relations between the EU and Russia.
Ultimately, Finland’s entry into NATO can be seen as a sign that the alliance continues to expand and strengthen amid rising tensions with Russia. This could be interpreted as a military escalation in the region and could prompt a response from Russia. However, supporters of Finland’s NATO membership argue that the move is necessary to ensure the country’s security in the face of increasing Russian aggression in the region.




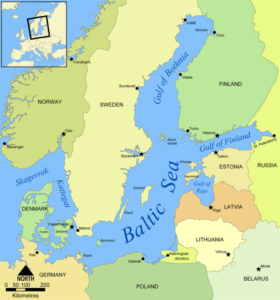






[…] of major changes, with implications that reverberate beyond its waters. The entry of Sweden and Finland into NATO marks a historic turning point, challenging decades of neutrality and redefining the region’s […]
[…] BRICS represents the initial of the name of each of the group’s countries, being Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. They are considered emerging countries in a developing situation, […]