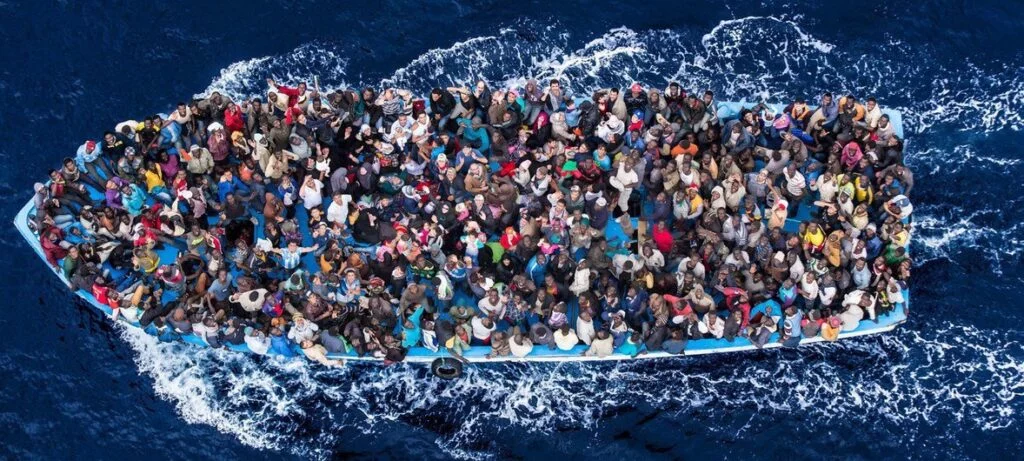
- Waters that were once trade routes and historic connections have now become the scene of desperate migratory movements;
- In 2023, more than 100,000 migrants have already reached Italy via the Central Mediterranean route;
- IOM plays a crucial role in humanitarian aid and geopolitics, crossing borders and influencing international dynamics.
In the midst of a constantly changing global scenario, the International Organization for Migration (IOM) emerges as a prominent entity, whose role transcends borders and reverberates in the complex geopolitical dynamics.
As Mediterranean routes witness desperate migratory movements and once-calm waters become the stage for monumental humanitarian challenges, IOM finds itself at the epicenter of this evolving crisis.

What is the IOM and what kind of support does it offer migrants?
IOM plays a crucial role in supporting migrants in crisis and emergency situations. Founded in 1951, this intergovernmental agency that is part of the United Nations UN system, has as its main mission to coordinate the humanitarian response and international cooperation to deal with migration challenges on a global scale.
The international organization focuses its efforts on providing direct and responsive assistance to migrants, regardless of their status – refugees, internally displaced persons, asylum seekers or migrant workers.
In the vision of the Principles for Humanitarian Action are the four essential humanitarian principles:
- The principle of humanity – humanitarian action is motivated by the intention to help those affected by crises, and solely and exclusively for that reason.
- The principle of impartiality – humanitarian assistance and protection are offered without discrimination, based on people’s needs, and needs only, on a proportionate basis.
- The principle of neutrality – humanitarian action is conducted without favoring any of the parties involved in the conflict.
- The principle of autonomy – humanitarian action is carried out without any influence from political, military, economic or any other interests.
IOM acts as a mobilizing force in critical moments, ensuring that the human rights and dignity of these people are protected even in the most adverse circumstances.
This encompasses concrete actions such as the provision of shelter, medical care, food supplies, access to clean water, legal protection and psychosocial support.
Who are migrants and what are their rights?
Migrants are a diverse group, including refugees, internally displaced persons, asylum seekers, workers and students seeking a new life in other countries. Their motivations range from refuge from conflict to better economic opportunities.
On the international scene, their rights have been discussed. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) established the principle of equal dignity and rights, regardless of nationality or immigration status.
In the case of refugees, the United Nations Convention relating to the Status of Refugees (1951) and its Protocol (1967) define a vital legal framework to protect them, ensuring the right to seek asylum and protection against dangerous repatriation.
The “International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families” (1990) also provides guidance on the rights of migrants who have sought asylum and need to work.
However, the implementation and guarantee of migrants’ rights face significant challenges. Restrictive migration policies, xenophobia, religious prejudice and bureaucratic barriers can obstruct the protection of migrants’ rights.
However, it is important to point out that people who migrate purely for economic reasons do not necessarily have the right to reside and work in the country of destination legally, and theoretically could be deported.
These restrictions are due to negative reactions from natives, who may see economic migrants as a threat to local jobs and resources.
What are the current challenges facing the IOM in light of the migratory crisis in the Mediterranean?
The migration crisis in the Mediterranean involves a critical humanitarian situation faced by refugees from Africa, the Middle East and Asia, who seek to reach Western Europe.
In 2023, more than 100,000 migrants have already reached Italy via the Central Mediterranean route, and the country is on the verge of surpassing the total registered throughout 2022.
The crisis reached its first peak in 2015, with an exponential increase in refugees for economic reasons or fleeing conflict, climate disasters, human rights violations and oppression.
However, we have seen a significant increase in the number of migrants risking or losing their lives in the
in 2023. Illegal trafficking groups exploit these vulnerable migrants, exacerbating the situation, to the point where one fisherman says it is common to find bodies in his net.
The crisis results from the growing number of irregular migrants seeking to reach the European Union, through dangerous crossings in the Mediterranean Sea and through the Balkans. It is the biggest humanitarian crisis faced by Europe since the Second World War.
Waters that were once trade routes and historic connectivity have now become the scene of desperate migratory movements, unleashing significant political and humanitarian pressures on the IOM.
According to the European Council, the routes most used by migrants are:
- The Western Route
- The Central Route
- The Eastern Route

In 2023, until the writing of this article, there were 87,313 arrivals of irregular migrants. The number of arrivals by migratory route breaks down as follows:
- Central route: 65 571 arrivals
- Eastern route: 13,167 arrivals
- Western route: 8,575 arrivals

In June 2023, unfortunately, we had the biggest shipwreck of the year so far. Reports indicate that approximately 400 to 750 individuals had crammed into the fishing vessel which capsized and sank in deep water, about 50 miles (80 km) off the southern Greek coastal town of Pylos. Greek authorities reported that only 104 survivors were rescued.
One of the main concerns facing the IOM is the impact of political pressures and obstacles to the implementation of effective migration policies. In a region where the migration issue is often intertwined with internal and external political agendas, coordination between coastal and cross-border countries has become an extremely difficult task.
Differences over the distribution of responsibilities, the establishment of consistent asylum policies and the management of migration flows have challenged IOM’s efforts to ensure a unified approach.
Despite its efforts, the organization has been the target of criticism regarding its ability to deal with the massive migratory flows that reach the shores of the Mediterranean.
The demand for human, financial and logistical resources to provide adequate assistance and protection to migrants often exceeds available means. This discrepancy between need and capacity often exposes IOM to accusations of inadequacy in responding to urgent humanitarian situations.
Another significant challenge lies in the tensions between the need to ensure security and order at borders and respect for the human rights of migrants. Search and rescue operations at sea, for example, can be complicated by political and legal constraints, leading to preventable tragedies and questions about liability.
How does the IOM try to balance national and humanitarian interests?
Despite the various rights guaranteed to migrants, IOM faces the ongoing challenge of reconciling national interests of the countries that receive the most migratory flow, with humanitarian guidelines amidst the current global scenario full of armed conflicts and economic crises.
With the constant pressure to find a balance between respect for the sovereignty of States and the need to protect and support vulnerable migrants, IOM has developed strategies to address this dynamic.
A key approach adopted by the IOM is the development of sustainable programs that aim to meet the needs of both countries of origin and destination countries.
Some concrete examples of IOM sustainable programs include:
- Skills development and training: The agency works with countries of origin to provide training and capacity building to potential migrants, preparing them for work opportunities abroad. Not only does this benefit migrants by offering them the chance for better, better-paying jobs, but it also contributes to the economic development of the home country by improving the skills and productivity of the workforce.
- Knowledge transfer and remittances: IOM promotes the positive use of remittances sent by migrants back to their countries of origin. This may involve actions such as developing investment programs or development projects that are funded by remittances. This helps direct migrants’ financial resources towards initiatives that benefit their home communities by improving infrastructure, education, health and other sectors.
- Sustainable return and reintegration: The organization works to facilitate the voluntary and dignified return of migrants who wish to return to their countries of origin. This may include providing financial assistance, training and support for reintegration into their home communities. The aim is to allow migrants to use their experiences and skills acquired abroad to contribute to the development of their home nations.
- Regional cooperation: IOM encourages cooperation between countries of origin, transit and destination to develop joint strategies to manage migration flows. This may involve creating programs that allow for legal and safe migration, as well as the exchange of information to combat human trafficking and the exploitation of migrants.
By investing in development projects, the organization aims to minimize the underlying reasons for migration, while creating economic and social opportunities for local communities. This not only helps alleviate migratory pressure, but also contributes to equitable growth and stability in different regions.
In addition, IOM strives to respect the national sovereignty of each country, recognizing that border management and the formulation of migration policies are the prerogatives of States. However, through constructive dialogue and cooperation with governments, the organization seeks to facilitate implementation of measures that address migration issues in a manner compatible with national interests.
Another crucial point is the fight against human trafficking and the exploitation of migrants. IOM plays an active role in raising awareness, preventing and intervening against these deplorable practices.
Why is IOM important for Geopolitics?
The IOM is a key player in geopolitics, as it crosses borders and has the power to influence international dynamics.
One of the main reasons for the geopolitical importance of the IOM is its ability to analyze migration trends and their impacts. By collecting data and information on the movements of people on a global scale, the organization offers valuable insights into the motivations, patterns and destinations of migrants.
These informed analyzes not only inform policies and internal decisions of different countries, but also help in anticipating future challenges and formulating strategies to face them.
The management of migration flows is another critical dimension in which the IOM exerts its geopolitical influence. Through search and rescue operations, humanitarian assistance and resettlement, the organization plays an active role in mitigating migration crises.
Humanitarian diplomacy is also an essential facet of IOM’s geopolitical influence. By acting as a mediator and facilitator on migration issues, the organization promotes dialogue and international cooperation. This helps build bridges between countries and promote agreements that aim to protect the rights of migrants, while respecting the legitimate concerns of States.
For example, during the Syrian refugee crisis, IOM played a crucial role in facilitating agreements between countries and different actors in the conflict region for the relocation of refugees and providing essential humanitarian assistance to the displaced.
The organization also plays a significant role in shaping international policies related to migration. Through its participation in global forums and collaboration with other international organizations, IOM influences the agendas and guidelines that shape the regulatory framework and collective approach to addressing migration challenges.
Finally, its capacity for analysis, management, diplomacy and influence on international policies make IOM a respected and necessary voice in a world where mass migration is increasingly proving to be a dilemma in International Relations.




Be First to Comment