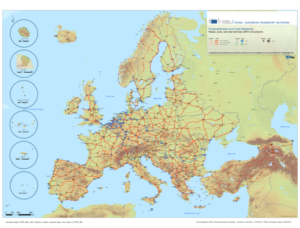
Since 2016, the “Three Sea Initiative” (3SI), which brings together 12 Member States of the European Union on Central and Eastern Europe, has been building a financial and investment support project.
The programme has this name because of the Adriatic Sea, the Baltic Sea and the Black Sea. It is the junction of Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia.

What is the Three Sea Initiative
3SI is an infrastructure investment fund project in Central Europe, designed in 2015 and led by Poland and Romania with an investment of 500 million euros in transport, energy and technology.
From the first summit in 2016, there is a prospect of bringing together private investors and pension funds to raise around 3 to 5 billion euros. In 2017, former President Donald Trump attended the Initiative meeting and was enthusiastic about the project, in addition to promising help with the private market to raise this income. In February 2021, US Secretary of State Antony Blinken reaffirmed the position of the Biden administration.
Common infrastructure projects of the initiative
The project has 48 staves. The main structures that have investments are in roads and viaducts that connect the North and South of Central Europe, as well as natural gas pipelines by the Member States of the 5G initiative and implementation in the region by “Three Seas Digital Highway”.
The purpose is to recover a post-World War II historical delay and how the battle affected the structural development of the region.
With the material objective of infrastructure development, the policy objective is:
“make Central Europe the backbone of European resilience,” and move the newer member states of the European Union (EU) closer to economic convergence with their Western neighbors.
Grabar-Kitarović (ex-president of Croatia), 2018 Bucharest Summit
Geopolitical implications of the 3 Seas European Initiative
The establishment of the investment fund by a group of EU countries appears as a response to the Chinese and Russian advance in the Central European area.
The worldwide infrastructure works investment project “Belt & Road Initiative” of China was advancing in the countries furthest from the European economic centers, building ports and highways in the region in addition to securing credit loans to countries as a way to gain new economic allies, the so-called “debt trap” or “diplomacy of debt.”
In addition, several Member States participating in 3SI have borders with Russia and its allies. The Russian-EU relationship is in a fragile state, and this is an attempt to provide financial support to these countries coming from the Union itself and not from Russia.
Thus, with the support of the US and its common interests to strengthen Central Europe’s relations with the West, moving it away from the East, there is this great effort to ensure the provision of infrastructure and finance.
It is another action within the European Union seeking to reaffirm itself for the international scene, as well as for these 12 States, of which the Union is there to provide support and base, without the need to establish new socioeconomic contracts with other powers.
It is a way for the EU to strengthen itself as an active and united group in the geopolitical scenario.
















[…] following the model of Three Seas Initiative, Bucharest Group 9 aims at increased investment by the European Union in having a more active […]
[…] creating the Visegrad International Fund. It is an international organisation, similar to a Three Seas Initiative, of donors for the development of the institutions of Central and Eastern Europe and is the only […]
[…] are several developmental projects currently underway by the EU, such as the Global Gateway and a Three Seas Initiative. […]
[…] there has been a search for security plans, in case there is a cut in Russian supply, through a strengthening of European internal energy integration, increasing solidarity relations between States-membership, and external renegotiation of the […]
[…] addition, deepens international relations with other nations so that it can stimulate Chinese industries and increase the country’s geopolitical power. Thus, […]
[…] forms, such as by direct association (these countries becoming members of NATO or EU) or via developmental plans financed or supported by those same […]