On 21 January 2022, Iran’s Foreign Minister Hossein Amir-Abdollahian visited Beijing to discuss the implications of the strategic Sino-Iranian cooperation agreement.
The relationship between China and the Middle East is a fertile field for partnerships by China’s energy interest and trade relations in general, as in the examples of partnerships via a Belt & Road Initiative (the “New Silk Road”), of which Iran is a part.
However, this strategic partnership between China and Iran has several implications in the geopolitical scenario and, mainly, with the interests of the United States and Israel.

Trade partnerships between China and Iran
In March 2021, China and Iran signed a 25-year partnership on nuclear technology exchanges for peaceful, energy, and infrastructure purposes (as well as military ones). With this, billions of dollars from China are invested in Iranian development in exchange for oil cheaper than the market price.
China and Russia, in September 2021, defended and approved the inclusion of Iran in the partnership of the Eurasian countries, Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO).
The SCO’s main goals are as follows: strengthening mutual trust and neighbourliness among the member states; promoting their effective cooperation in politics, trade, the economy, research, technology and culture, as well as in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, and other areas; making joint efforts to maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region; and moving towards the establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political and economic order.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
Iran’s “look to the East” will bring not only development to your country but also an ally against US sanctions. China, making a deal with the Iranian government, gains another alliance in the Middle East, strengthening itself; guarantees an agreement with the country that owns 20% of oil reserves, as well as commodities; and gains support against US actions.
Military partnerships between China and Iran
The 25-year agreement between the two countries has clauses in secret, but it was reported that exchanges of information and intelligence, military corps and arms development were negotiated.
In addition, the inclusion of Iran in the SCO has increased its relationship with other powers, such as Russia. In 2019, the partnership between the countries acted jointly in the Indian Ocean and the Gulf of Oman and in 2021/22 Moscow, Beijing and Iran plan to act in union of military forces in the Persian Gulf.
Chinese investment in Iranian development also allows for growth in the production of Iran’s nuclear weapons. This growth is causing the most political insecurity for the US and Israel, mainly because China advocates a decrease in US sanctions and a reform in Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, JCPOA.
The JCPOA is the famous Iranian Nuclear Agreement where the major world powers have reached an agreement with Iran to ensure that its nuclear program is peaceful and never used for military purposes. In exchange for the Iranian commitment, several sanctions against the country were taken.
However, Iran’s peaceful nuclear development brings China an advantage, as it could invest in the country without challenging the sanctions imposed by the United States.
The implications of the Sino-Iranian partnership for the US and the world
The Sino-Iranian partnership is not only based on economic and military principles, but also political.
Since 2017 and the beginning of the Trump administration, there have been several sanctions after the request for revision of the JCPOA by Iranian initiative. With Chinese investment, the effects of these sanctions are mitigated, which will increase to a Sino-Iranian “intransigence” in the discussions on nuclear potentials and the JCPOA.
However, there is a Chinese security ambiguity, mainly with its relations with other countries of the Arabian Gulf and Iran at the same time, as there are internal political issues that do not please all parties. With American sanctions, this ambiguity is even more difficult.
After the end of the conflicts in Afghanistan and Iraq, there was a decline in the US presence in the Middle East, which allowed this growth of Chinese influence. This aggrandizement threatens US, Israeli and EU socio-political relations with the region, especially in the peaceful withdrawal of US troops in Afghanistan.
Iranian infrastructure and nuclear development is not within US interests, on the contrary. In 2019, Iran announced that it had begun to increase uranium enrichment beyond the agreed JCPOA limit of 3.67%.
Military growth in the Middle East, especially in partnership with China, affects conflicts such as the Palestinian-Israeli one that has US support, as well as being an advantage in negotiating new alliance agreements. It is a geopolitical growth that threatens the position currently occupied by the United States.
China’s continued trade and investment with Iran provides a critical economic lifeline to the Iranian regime, reducing the efficacy of U.S. sanctions. China’s long-term investment in regional connectivity and continued interest in accessing Iranian resources means China benefits from an economically and politically stable Iran. Though China’s trade and investment with the regime contributes to the welfare of the average Iranian citizen, it also emboldens the Iranian regime to continue its malign activities in the face of international pressure.
US-China Economic and Security Review Commission
How it Affects Iran’s Nuclear Agreement (JCPOA)
The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, the “Iranian Nuclear Deal” was made in 2014 by Iran and the 5 permanent UN Security Council countries (China, France, Russia, the UK and the US) together with the European Union, the P5+1. The Plan has 109 pages, the main guidelines being addressed on the limitations of Iranian nuclear production and research:
- Eliminate the stockpiles of enriched uranium;
- Eliminate 98% of your enriched uranium reserves;
- reduce the number of gas centrifuges by two-thirds over a maximum period of 13 years;
- In the fifteen years agreed, Iran can enrich uranium only 3.67%;
- Iran will not be able to build specialized nuclear power plants during the fifteen years;
- Enriched uranium activities will be limited to one plant for ten years;
- Other plants will be reformed to avoid proliferation risks;
- The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) will monitor the country’s energy activities and will have regular access to nuclear power plants;
- Iran should receive sanctions from the United States, the European Union and the United Nations Security Council.
However, in 2018, former US President Donald Trump left the JCPOA and applied sanctions against Iran.
The China-Iran Agreement discusses the role that China should play in the reform of the JCPOA, especially in the area of American sanctions discussions, since this hinders the establishment of its trade and political alliance. The Chinese position is firm in the re-establishment of the agreement, but that there are reforms so that Iranian interests can be realized.
China is more a supporter of the JCPOA than the Iranian position writ large. Its support comes less out of concern for Iran’s nuclear motivations (presumably Chinese leaders understand that the Iranian government is not suicidal), but rather as a way of resolving tensions between Iran and the United States, in order to remove the sanctions against Iran. Sanctions are the main impediment to implementing the 25-Year Iran-China Agreement and improving economic ties between the two countries. Chinese investors are historically unlikely to be interested in Iran unless sanctions are lifted.
The Diplomat
What is the “Chinese White Area Warfare”
The 25-year agreement between China and Iran is part of the “Chinese white warfare area” , of strategic alliance military advantages. This means that even if it were a simple trade alliance of the Belt & Road Initiative, China is becoming more important in the Gulf and Middle East area.
Actions like these make greater profit, but more important: an expansion of influence from China.
With the investment in these areas, there is the creation of an alliance but also of a dependency that brings economic, political, social and military advantages to the Chinese side. It is an expansion of its ideological and social project that gradually changes the relations between countries.
This “white warfare area” is the basis of the project of gaining geopolitical power, that, at small steps and forming alliances with the countries, there is the ambition to take the reins of the United States on international relations.


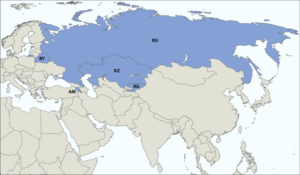

















[…] program. With the purpose of increasing economic relationships with countries on the South of Asia, Middle East and North Africa, the Chinese government intends to invest about US$4 trillion (about US$1 trillion […]
[…] and Iran (investment recipients of China’s Belt & Road development initiative) have built two […]