- Importing Liquefied Gas can be a solution to part of the energy crisis in European countries.
- Increasing use of floating LNG terminals facilitate gas imports and increase diversification of energy sources
- LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) and the new, more flexible processing terminals are revolutionizing the world energy sector.
LNG (liquefied natural gas) terminals play a strategic role in the security of natural gas supply, as they promote supply flexibility and diversify supply sources in the energy market.
Energy dependence between nations is a factor that moves world geopolitics, making evident the strong relationship between these two sectors, since energy security is a fundamental part of geopolitics.
If the political and energy relations between the countries are considered, one can easily perceive the dependence between States and the accentuated centralization in some sources, such as fossil fuels: oil, natural gas and coal. Since more than 80% of the world’s energy matrix still comes from fossil fuels in 2022.
Therefore, LNG terminals that can be produced and transported more flexibly and quickly are increasingly playing an important role in the energy dynamics of large energy consumers to diversify their energy sources.

What are floating LNG terminals and how do they work?
The liquefaction of natural gas is the most efficient way to transport it over long distances by sea when there is no option for land gas pipelines. For natural gas to be exported as LNG, there is a global fleet of modern tankers known as methane tankers.
This is a type of vessel capable of storing and transporting the product to floating terminals, and once the gas arrives at its destination, which has treatment points, the LNG undergoes a process of regasification.
In recent years, the LNG market has been expanding and it is expected that the demand for liquefied gas will still increase by 25-30% until 2030. This increase derives from factors such as the expansion of liquefaction and regasification technology and the increase in demand for cleaner energy.
By 2022, the United States has become the world’s leading LNG producer and largest exporter. The EIA (Energy Information Administration) report estimated that US LNG exports average 11.2 billion cubic feet per day. The daily average for the first six months of 2022 was 12% higher than for the second half of 2021.
Therefore, investment in new floating terminals has been of great importance for the energy sector, as they facilitate the marketing of LNG because they are more flexible, economical (compared to fixed terminals) and because they can reach, in particular, where terrestrial gas pipelines are not used.
How do floating LNG processing terminals ease geographic restrictions for natural gas trading?
With the gradual increase in natural gas liquefaction structures and LNG regasification terminals around the world, it is becoming possible to remodel the energy sector due to the new range of options that exporters and importers of natural gas now have.
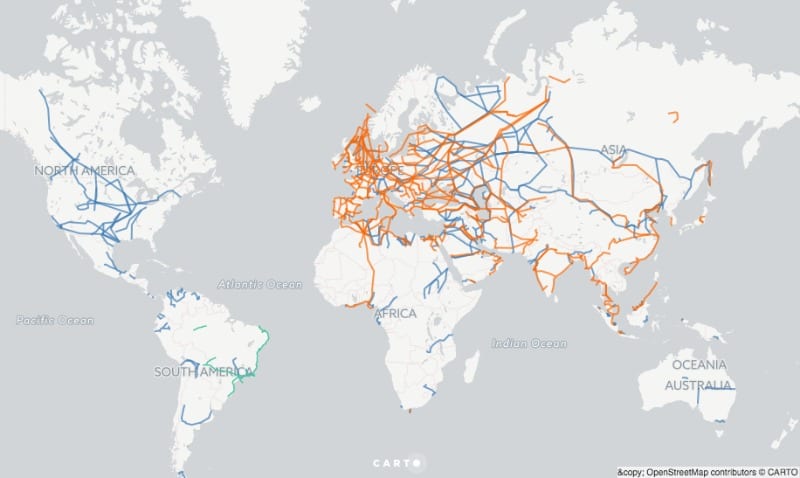
Natural gas in its gaseous form has physical export borders due to the gas pipeline network required to transport the fuel, as illustrated in the image below. Therefore, exporting between continents becomes extremely expensive and even not advantageous.
In the case of LNG, once the gas goes through the liquefaction process, it can be transported anywhere in the world. From this perspective, this method becomes revolutionary, as export borders cease to exist and gas trade between continents becomes possible.
As an example, we can analyze the sudden increase in the export of natural gas from the United States to Europe, in the midst of the European energy crisis accentuated by Russia’s war in Ukraine.
Due to Western economic sanctions applied to Russia, Vladimir Putin decided to indefinitely cut the gas with which Moscow supplied the European continent, via the Nord Stream 1 gas pipeline.
That said, there is an energy vulnerability due to geopolitics, which could not be easily resolved without the option of using the new floating LNG terminals, responsible for receiving almost 50% of all gas imports by the European continent, in 2022.
It is true that American LNG cannot solve the European energy crisis, but it is expected to be enough for citizens not to freeze in the harsh winter due to lack of gas for their heaters.
This high demand and low supply of gas has driven European Union countries to apply efforts to further develop European liquefied natural gas terminals, while at the same time depending on terminals floating gas stations as an emergency measure to meet their needs.
What are the negative and positive points of importing LNG as a substitute for natural gas via pipelines?
One of the main drawbacks of importing LNG is its high cost. This cost derives from the necessary infrastructure for liquefying, storing, transporting and regasifying the gas.
The very low temperatures, around -162ºC, demand specific materials that support the storage of LNG, avoiding the dangers of leaks and suffocation for the team. In addition to a larger storage space, up to 150% of fuel oil storage space.
However, the good points of LNG make the higher cost and infrastructure worth it. This is because liquefied gas is cleaner than other natural gases, favoring the environment.
LNG produces 40% less carbon dioxide (CO2) than coal and 30% less than oil, making it the cleanest of all fossil fuels.
LNG also does not produce particulates and dust, in addition to emitting almost negligible amounts of sulfur dioxide, mercury and other compounds considered harmful to the Earth’s atmosphere.
However, although LNG is less harmful to the environment than natural gas, in the long term the best solutions for an energy transformation still come from renewable energy sources rather than fossil fuels.
In addition to LNG, floating terminals have benefits that conventional terminals could not offer, such as: reaching smaller areas and avoiding the simultaneous construction of traditional terminals, which guarantees greater security in energy supply.
The importance of floating LNG terminals to increase the energy resilience of importing countries and its geopolitical consequences
Dependence on only one energy source generates great vulnerability in the energy sector, especially when it comes to a national or continental level of dependence, as in the most evident case of 2022: Europe.
Therefore, liquefied natural gas is a possibility of diversifying the supply of gas to countries that need to import energy, and the new floating terminals make the sector more resilient and able to adapt to adverse situations, such as geopolitical conflicts that can affect the economic and energy sectors.
Taking the European Union as an example, but not limited to it, it is observed that LNG has the important and necessary capacity to improve the continent’s energy security and sovereignty.
European countries that in the midst of war in Ukraine have access to LNG import terminals and liquid gas markets are much more resilient to supply disruptions than those that rely on a single gas supplier or a single other energy source.
As a consequence, the access to a greater diversity of suppliers around the world that floating LNG terminals offer can not only reduce prices, but also offer importing countries the flexibility to change trading partners and greater energy autonomy.
Therefore, with LNG as an energy source option and floating terminals in greater use, suppliers around the world will be able to close trade agreements with countries they consider more reliable and even avoid markets with potential security and supply risks.
Finally, the increased investment and use of floating Liquefied Natural Gas terminals has been a watershed for world energy trade, bringing the continents even closer in terms of energy dependence, in addition to contributing to the alleviation of the energy crisis in countries with shortages, not to mention the benefit of reducing the environmental impact when gas replaces more polluting energy sources.







[…] sustainable energy transition is, without a doubt, one of the world’s greatest concerns in search of the good of the […]
[…] Guyana is also preparing to exploit its natural gas reserves, envisioning the next energy frontier. This production is particularly relevant for Europe, which […]
[…] Guyana is also preparing to exploit its natural gas reserves, envisioning the next energy frontier. This production is particularly relevant for Europe, which […]