- The Belt and Road Initiative, launched by China in 2013, seeks to establish an extensive global infrastructure and trade network.
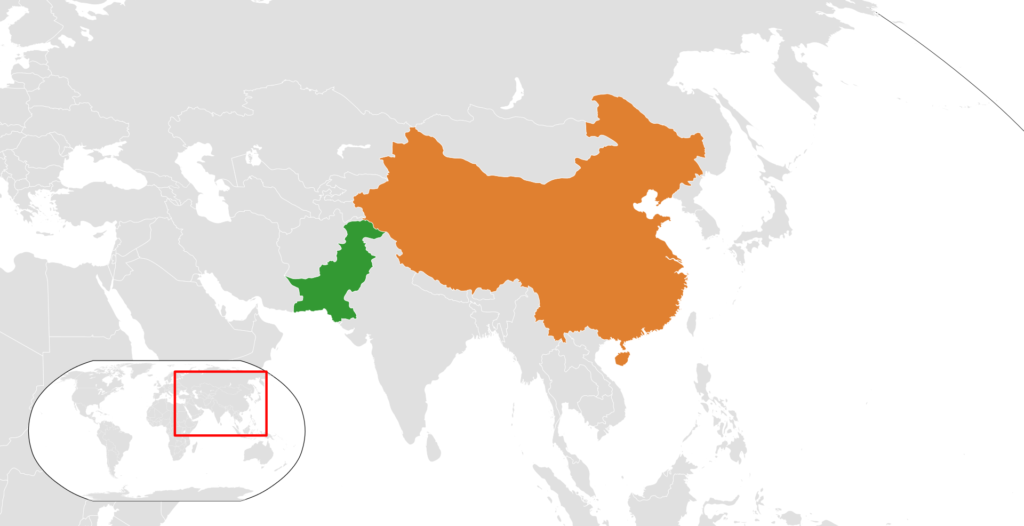
- The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is one of the highlights of this initiative, boosting economic objectives and raising transparency and security concerns.
- CPEC is a far-reaching geopolitical project, redefining regional and international relations in South Asia.
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor plays a crucial role in China’s ambitious Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a global-scale development project. This is a multifaceted project that has far-reaching implications that go beyond economic and infrastructure issues.
Therefore, it is essential to carry out a comprehensive geopolitical analysis, examining its impact on regional and global dynamics, as well as its influence on maritime shipping routes.
What is the Silk Road?
For centuries, the Silk Road has been a symbol of connection, trade and cultural exchange between East and West. This network of intercontinental trade routes, dating back to the second century BC, played a key role in the exchange of goods, technologies, religions and ideas between East Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, Africa and Europe.
The name “Silk Road” is a reference to the valuable silk fabrics that were transported along these routes, although a wide variety of products, such as spices, ceramics, precious metals, and even knowledge, were traded over time.
The Silk Road was one of the greatest milestones in the history of global trade and played a pivotal role in shaping the modern world.
Today, the story continues, as China revitalizes this ancient route with its ambitious global connectivity project known as the Belt and Road Initiative (also called the New Silk Road).
The New Silk Road: China’s 21st Century Vision
The Belt and Road Initiative, launched by China in 2013, is a massive development project that aims to establish a network of infrastructure, trade and connectivity that spans various regions of the world.
This initiative aims to strengthen trade relations, improve transport and energy connectivity, and promote economic and cultural cooperation on an unprecedented scale.
The New Silk Road is made up of two main parts: the Silk Road Economic Belt, which focuses mainly on land connections, and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, which focuses on sea routes.
Both aim to strengthen trade and cooperation between China and partner countries along the routes, promoting economic development and regional stability.
What is the objective of the Sino-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) and what are its main works?
In order to provide greater clarity about the ambitions of both governments, we can examine the main purposes and the most prominent works of this corridor.
CPEC Objectives:
- Connectivity: The project aims to improve land and sea connectivity between China and Pakistan. The Karakoram Highway is a notable example, being the highest paved road in the world, connecting the two nations at an altitude of 4,693 meters. This reduces the distance and time for transporting goods between the two countries.
- Economic Development: also aims to promote economic growth in Pakistan. This is achieved through investment in infrastructure, which creates jobs and stimulates trade and investment, improving the country’s economy. Furthermore, regional development projects aim to reduce economic disparities in the country.
- Access to Ports: A crucial part of CPEC is the development of Gwadar Port, which provides China with easier access to the Indian Ocean. This is significant for China as it reduces the distance from Western China’s trade routes, saving time and resources.
- Energy: The project addresses Pakistan’s energy needs. This includes the construction of power plants such as coal-fired power plants and hydroelectric plants. These plants help combat the energy crisis in Pakistan by providing electricity to areas that face frequent power cuts.
- Industrialization: It also aims to stimulate industrialization in Pakistan. This involves establishing special economic zones (SEZs) to attract foreign investment, encourage the manufacturing sector and promote the export of Pakistani products.
- Regional Development: The project has a significant focus on the development of less developed regions of Pakistan. Infrastructure projects such as roads and railways are extended to these areas, improving connectivity and economic opportunities.
Main CPEC Works:
- Karakoram Highway: The Karakoram Highway is one of the most iconic works of CPEC, connecting Kashgar, China, to Gwadar, Pakistan. It crosses mountains and is the highest paved road in the world.
- ML-1 Railway: Pakistan’s main railway modernization project, known as ML-1 Railway, aims to improve rail transport of goods and passengers. With China’s support, this should improve transport infrastructure in Pakistan.
- Gwadar Port: Development and expansion of Gwadar Port is also a key part of CPEC. This aims to transform the port into an important logistics center, facilitating international trade.
- Power Plants: Several power plants are being built as part of CPEC, including coal-fired plants and hydroelectric plants. These plants address the growing demand for energy in Pakistan.
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs): The establishment of SEZs is a crucial part to stimulate industrialization. SEZs provide incentives for companies wanting to invest and operate in Pakistan, which boosts the manufacturing sector and production.
These combined projects and objectives have the potential to transform Pakistan economically and strengthen ties between China and Pakistan.
However, the Belt and Road Initiative also faces criticism and challenges. Furthermore, geopolitical issues and regional rivalries may complicate the effective implementation of the initiative.
What are the Criticisms and Challenges of the China-Pakistan Corridor?
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is an ambitious project that aims to strengthen economic and strategic ties between the countries. However, as is common with initiatives of this magnitude, CPEC also faces significant criticism and challenges.
One of the main criticisms of CPEC is the issue of transparency of Chinese loans. Many observers argue that the project lacks transparency in terms of financial arrangements and details on the terms of loans extended by China to Pakistan.
This lack of transparency has raised concerns about the high debt accumulated by Pakistan towards China, which could affect its economic sovereignty. This is a common problem with many of China’s Silk Road partner countries, leading analysts to accuse Beijing of creating “debt traps” with its partners.
Furthermore, CPEC faces concerns over environmental issues. The construction of coal-fired power plants and other infrastructure projects has led to concerns about environmental degradation and increased greenhouse gas emissions. This raises questions about China’s commitment to sustainable environmental practices.
Another important challenge is security. CPEC passes through regions of Pakistan that face instability and conflict. Attacks on Chinese infrastructure projects and workers have been a recurring concern, particularly in the Balochistan region. As such, safety along the route remains a critical issue.
Furthermore, the project faces geopolitical challenges. The close ties between China and Pakistan have raised concerns in other countries, particularly India, which sees the project as a Chinese strategy to expand its regional influence.
Although CPEC has the potential to bring substantial economic benefits to Pakistan, these criticisms and challenges cannot be ignored. Overcoming these obstacles will require continued efforts from both nations and a careful approach to ensure that the project serves the long-term interests of both parties and is beneficial to regional stability.
Why is CPEC geopolitically important?
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor is a geopolitically important undertaking for several reasons, the implications of which extend beyond economic and infrastructure issues.
Here are the main reasons that highlight its importance in the geopolitical scenario:
- Expanding Chinese Influence: CPEC is central to China’s strategy to extend its influence in Asia and globally. By establishing a direct connection between China and the Indian Ocean through Gwadar Port, China reduces its dependence on longer and potentially vulnerable trade routes, consolidating a more robust geopolitical presence in the region.
- Challenge to Indian Dominance: CPEC’s geographic proximity to India has significant geopolitical implications. India considers parts of CPEC to be part of its Pakistan-controlled territory of Jammu and Kashmir. This creates tensions in geopolitical relations in the region, involving India, China and Pakistan.
- China-Pakistan Partnership: CPEC strengthens the strategic partnership between China and Pakistan, consolidating bilateral relations and influencing geopolitical dynamics in Asia, particularly in relation to other regional actors such as India, the United States and neighboring nations.
- Stability in Pakistan: Pakistan’s internal stability is crucial for China, given its concerns about the security of its investments. Any political or security instability in Pakistan has significant implications for how China handles internal and security issues in the country.
- Impact on West and Central Asia: CPEC can influence economic dynamics in West and Central Asia, allowing these regions to access the Chinese market more effectively. This has geopolitical implications, as countries like Iran and Central Asian nations could be affected by the evolving regional balance of power.
- US Interests: The United States closely monitors CPEC, due to its strategic ties with Pakistan and the quest to contain the expansion of Chinese influence.
- Maritime Geopolitics: CPEC significantly affects maritime geopolitics, allowing China to diversify its navigation routes. Access to Gwadar Port reduces China’s dependence on the Strait of Malacca, a strategic passage where much of its imports occur. This diversification of maritime routes reduces China’s vulnerability to conflict or blockages in the Strait of Malacca and influences relations with other nations interested in the security of this passage.
In short, CPEC is an initiative that influences beyond infrastructure and trade, playing an important role in the complex geopolitical dynamics of the region, potentially reshaping the balance of power between nations in Asia and globally.






Be First to Comment